These naturally occurring elements are essential in everything from wind turbines to lasers to iPads.
Rare earths are a conundrum for the environmentally conscious—they hold the key to green energies but create toxic waste when being separated away from other elements. "Just one wind turbine generating 3 megawatts of electricity requires 600 kilograms of rare earths for its magnets," a source told the United Kingdom's Guardian newspaper.
Electric and hybrid cars can contain more than twice as much rare earth metals as a standard car. The following image from the New York Times breaks down how these metals make up critical elements of a Prius.

Currently, China controls 97% of the world's production of rare earth metals. In October 2010, the country cut exports of the metals by 70%, disrupting manufacturing in Japan, Europe and the U.S., and sending the prices of these metals up 40%.
China also currently controls production, but the country only has 37% of the world's estimated reserves. This second visual published by the New York Times shows the identified rare earth metal deposits around the globe.
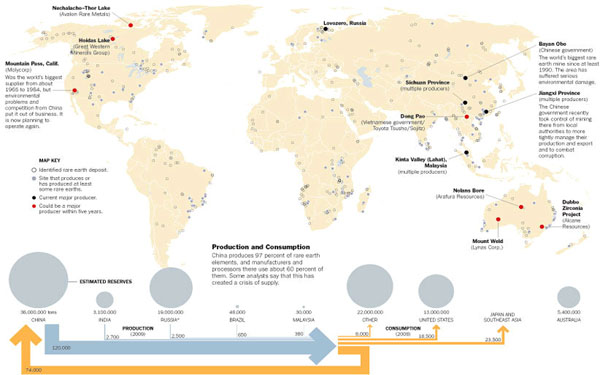
The U.S. used to be a top manufacturer of rare earth metals back in the 1960s, but eight years ago environmental infractions shut down the Mountain Pass, California mine—the largest deposit of rare earth metals outside of China. Currently, there are efforts to restart production at the mine but several hurdles must be cleared first. Today, the U.S. imports 87% of its rare earths from China.
Other countries such as Kenya, South Africa, Malawi and Greenland are believed to be sitting atop large deposits of rare earth metals, as well.
Increased production outside of China is required in order to meet rising demand. Estimates show that global demand is expected to reach 205,000 tons by 2015, according to the Guardian. As high-tech becomes a greater part of people's lives in both the developing and emerging world, the importance of these metals should continue to rise.